Navigating the Digital Landscape: Essential Computer Security Practices

In today’s interconnected world, where our lives are increasingly intertwined with the digital realm, computer security has become a paramount concern. As we rely on computers for work, communication, and entertainment, protecting our devices and data from cyber threats is crucial. Understanding the Landscape of Cyber Threats The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new and sophisticated methods emerging to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise systems. Common cyber threats include: Essential Computer Security Practices To safeguard your computer systems and data from these threats, it is essential to adopt a proactive approach to computer security. Here are some fundamental practices to follow: Additional Tips for Enhanced Security Beyond these essential practices, consider these additional measures to further enhance your computer security: Safe Internet Practices Educate Yourself and Stay Informed Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, making it crucial to stay updated on the latest trends and security practices. Follow reputable cybersecurity blogs, attend webinars, and consider certifications or courses to enhance your knowledge. Being informed empowers you to make better decisions when it comes to securing your digital assets. Securing Your Mobile Devices With the prevalence of smartphones and tablets, mobile security is equally important. Install security apps, enable device encryption, use secure Wi-Fi connections, and download apps only from trusted sources, such as official app stores. Business Security Practices About Computer Security For businesses, protecting sensitive data is paramount. Implement stringent security policies, conduct regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices, and invest in enterprise-grade security solutions to mitigate potential threats. Computer security is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and proactive measures. By adopting these essential practices and staying informed about evolving threats, you can significantly strengthen your defenses against cyberattacks and protect your valuable data. Remember, computer security is not just about protecting your devices; it’s about safeguarding your privacy, your finances, and your digital identity.
Defending Your Digital Fortress: A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security Attacks

Network security attacks have become an omnipresent threat, looming over organizations of all sizes and industries. As technology advances, so do the tactics employed by cybercriminals to infiltrate networks and compromise data. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of network security attacks, understand their various forms, and explore the strategies and tools to protect your digital assets. Understanding Network Security Attacks Network security attacks encompass a wide array of malicious activities aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities in computer networks. These attacks can result in unauthorized access, data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. To effectively defend against them, it’s crucial to understand their various forms: 1. Malware Attacks: Malware, short for malicious software, is a broad category that includes viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware. These programs are designed to infiltrate and damage computer systems, steal sensitive information, or extort money from victims. 2. Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks involve tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials or financial data. Attackers often use convincing emails or websites that appear legitimate to deceive their targets. 3. DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm a network or website with a flood of traffic, rendering it inaccessible to users. This can disrupt business operations and cause financial losses. 4. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: MitM attacks involve intercepting communications between two parties, often without their knowledge. Attackers can eavesdrop, modify data, or inject malicious content into the communication. 5. SQL Injection Attacks: These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in web applications by injecting malicious SQL queries into input fields. If successful, attackers can access or manipulate databases. 6. Zero-Day Attacks: Zero-day attacks target undiscovered vulnerabilities in software or hardware. Since these vulnerabilities are unknown to developers, they offer attackers a window of opportunity to compromise systems. 7. Insider Threats: Not all network security threats come from external sources. Insider threats involve malicious or negligent actions by employees or individuals within the organization, leading to data breaches or system compromises. Protecting Your Network Against Security Attacks Now that we’ve explored the various forms of network security attacks, let’s discuss strategies and tools to safeguard your digital fortress: 1. Install Robust Antivirus Software: Employ reputable antivirus software that offers real-time protection against malware, including viruses, Trojans, and ransomware. Ensure that the software is regularly updated to defend against emerging threats. 2. Keep Software and Systems Updated: Frequently update operating systems, software applications, and plugins. Cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities, so keeping your systems up-to-date is a fundamental defense. 3. Implement Strong Access Controls: Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. Limit access to sensitive data and systems only to authorized personnel. 4. Educate Your Team: Regularly train employees on security best practices, especially regarding email phishing. Create a culture of security awareness within your organization. 5. Use a Firewall: Employ a firewall to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls can block suspicious activity and protect against unauthorized access. 6. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS can detect and respond to security threats in real-time. These systems can help identify and mitigate attacks as they happen. 7. Conduct Regular Vulnerability Assessments: Perform routine network vulnerability assessments to identify and remediate potential weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. 8. Encrypt Sensitive Data: Utilize encryption for sensitive data at rest and in transit. This adds an extra layer of protection even if attackers manage to access your network. 9. Develop an Incident Response Plan: Create a clear and comprehensive incident response plan to minimize the impact of a security breach. Ensure all employees understand their roles in the event of an attack. 10. Back Up Data Regularly: Frequent data backups are crucial for recovery in case of a ransomware attack or data loss. Store backups offline or in a secure, isolated environment. In an increasingly connected world, network security attacks are an ever-present threat that organizations must address proactively. Understanding the various forms of attacks and implementing robust security measures is paramount to safeguarding your digital assets and maintaining the trust of your customers and stakeholders. As cyber threats continue to evolve, ongoing vigilance and investment in security are essential to defending your digital fortress. Stay informed, stay secure.
Unveiling the Critical Importance of Network Vulnerability Assessment

Data breaches and cyberattacks have become increasingly prevalent, safeguarding your network infrastructure is paramount. One of the essential tools in the arsenal of cybersecurity is Network Vulnerability Assessment. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the critical importance of network vulnerability assessments, how they work, and best practices to secure your digital ecosystem. Understanding Network Vulnerability Assessment Network Vulnerability Assessment, often abbreviated as NVA, is the process of identifying, analyzing, and mitigating vulnerabilities in a network infrastructure. It is a systematic approach to proactively pinpoint weaknesses that could be exploited by cybercriminals. By conducting regular vulnerability assessments, organizations can strengthen their security posture, comply with regulations, and protect sensitive data. The Significance of Network Vulnerability Assessment How It Works Network Vulnerability Assessment involves a structured process that includes several key steps: Best Practices for Network Vulnerability Assessment Network Vulnerability Assessment is an indispensable component of a robust cybersecurity strategy. By identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities proactively, organizations can safeguard their network infrastructure, maintain compliance with regulations, and build trust with customers and partners. Embracing best practices and a culture of security ensures that your digital ecosystem remains resilient in the face of evolving cyber threats. Stay vigilant, stay secure.
What Happened in MGM Resorts and How Could It Have Been Prevented?

Last Sunday and ironically after a couple of weeks later from Black Hat conference, MGM where this conference held, faced a cyber security attack. After this attack company market cap decreased nearly 1 B USD and since they chose to shut all systems down including web sites and slot machines lost tens of millions revenue in 5 days. Apart from that they needed to pay a ransom which is estimated to be around 100 million USD because in a similar case this late summer Ceasers Palace Entertainment paid 30 million USD as ransom. The attack is said to be a social engineering kind vishing attack. The attacker pretented to be a person working in MGM, called the help desk and made help desk reset the password belonging to that person. And afterwards using the credentials penetrated to the system and enrcrypted or stole critical data and informed the related people about what he did or had. It was that much easy. Are you prepared for this kind of attack? Or in case of this kind of breach you also prefer to shut all systems down like MGM did? There are plenty of things to do not to face this kind of breach and I am sure most of them are already in place in MGM. Then, what is missing? First, there seems to be an authorization process and it is manual, meaning a person has the right to give or reset a password for an employee. A person can easily be deceived with social engineering tactics. If there is an authorization process in your infrastructure which is not automated already you should be more awake or have a plan to automate it. You can not trust people or system, trust and security does not coexist. If we talk about security there should be zero trust. You should have segmentation, indeed micro-segmentation in place to protect your workloads. Apart from this minimum rights principle is quite important and must be implemented for any enterprise, for example there should be no permissive or unused rules on your firewalls or only needed admin rights be used for all kind of IT accounts. Cyber security has always been an issue in IT spending budgets and generally it is tried to cut down, however if you face this kind of attack you may lose your following tens of years’ security budget in one case like MGM. It may be too late to take action afterwards.
Emerging Network Threats: Staying Ahead in the Cybersecurity Game

In the interconnected world, where businesses rely heavily on digital infrastructure, emerging network threats pose a significant challenge to cybersecurity. As technology evolves, so do the tactics and strategies of malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities. To stay ahead in the cybersecurity game, organizations must understand the landscape of emerging network threats and take proactive measures to protect their assets and data. The Ever-Changing Landscape of Network Threats Network threats come in various forms, and they continue to evolve. What was considered a formidable threat just a few years ago may now be relatively easy to mitigate, thanks to advancements in cybersecurity. Here are some of the emerging network threats that organizations should be vigilant about: 1. Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Zero-day vulnerabilities are security flaws in software or hardware that are unknown to the vendor or the public. Hackers exploit these vulnerabilities before a patch or fix is available, giving defenders zero days to respond. These threats can be particularly devastating as they often go undetected until an attack occurs. To mitigate the risk of zero-day vulnerabilities, organizations should invest in vulnerability management tools and practices that include regular system scanning and threat intelligence feeds. 2. Ransomware 2.0 Ransomware has been a menace for years, but it’s evolving. Attackers are becoming more sophisticated, using advanced encryption techniques and targeting high-value assets. Ransomware attacks are not just about encrypting data anymore; they often involve data exfiltration and the threat of public data leaks. Protecting against ransomware requires a robust backup and disaster recovery plan, employee training in recognizing phishing attempts, and a proactive approach to patching and system security. 3. Supply Chain Attacks Supply chain attacks target vulnerabilities in third-party vendors or service providers to compromise an organization’s network. These attacks have gained prominence in recent years due to the interconnected nature of business relationships and the potential for cascading security breaches. To defend against supply chain attacks, organizations should vet third-party vendors, regularly assess their security posture, and implement network segmentation to minimize the impact of a breach. 4. IoT and OT Vulnerabilities As the Internet of Things (IoT) and Operational Technology (OT) become more integrated into business operations, they introduce new attack surfaces. Insecure IoT and OT devices can be exploited to gain access to critical networks and systems. Securing IoT and OT environments requires robust access controls, regular updates and patch management, and network monitoring to detect unusual behavior. Proactive Measures to Mitigate Emerging Network Threats Understanding the nature of emerging network threats is just the first step. Organizations must also take proactive measures to mitigate these threats effectively. Here are some strategies to consider: 1. Threat Intelligence Integration Stay updated on emerging threats by integrating threat intelligence feeds into your security operations. These feeds provide real-time information about the latest vulnerabilities and attack tactics, allowing you to adjust your defenses accordingly. 2. Employee Training and Awareness Human error remains a significant factor in successful cyberattacks. Regularly train employees on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing emails, creating strong passwords, and reporting suspicious activity promptly. 3. Patch Management Regularly update and patch software, operating systems, and firmware to address known vulnerabilities. Implementing a robust patch management process can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to exploits. 4. Network Segmentation Segment your network to limit lateral movement in the event of a breach. This ensures that even if an attacker gains access to one part of the network, they will have a harder time moving laterally to access critical systems. 5. Zero Trust Architecture Adopt a zero trust architecture, where trust is never assumed, and verification is required from anyone trying to access resources on your network. This approach minimizes the potential attack surface and enhances security. 6. Incident Response Plan Develop and regularly test an incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a security breach. A well-prepared response can minimize damage and downtime. The Role of Emerging Technologies While emerging network threats present new challenges, emerging technologies also offer innovative solutions. Here are some technologies that can help organizations stay ahead of network threats: 1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time to detect anomalies and potential threats. These technologies can automate threat detection and response, making it faster and more efficient. 2. Blockchain Blockchain technology can enhance security by providing a tamper-resistant ledger of transactions and data. It can be particularly useful in supply chain security and ensuring the integrity of critical data. 3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before granting access. This can help prevent unauthorized access even if login credentials are compromised. Emerging network threats are a constant challenge in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. To protect their assets and data, organizations must remain vigilant, stay informed about the latest threats, and adopt proactive security measures. By integrating threat intelligence, training employees, and leveraging emerging technologies, organizations can strengthen their defenses and stay one step ahead of cyber adversaries. Remember, in the world of cybersecurity, staying ahead is not an option; it’s a necessity.
Proactive vs. Reactive Security Hardening: Understanding the Key Differences

In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity is of paramount importance. As businesses and individuals alike rely more on technology, the risks associated with cyber threats continue to grow. To combat these threats, proactive and reactive security hardening strategies have emerged as essential components of a robust cybersecurity posture. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of proactive and reactive security hardening, exploring their key differences, and helping you understand why both are crucial for safeguarding your digital assets. Proactive Security Hardening Proactive security hardening is a preemptive approach to cybersecurity. It involves implementing security measures and best practices before any potential threats can exploit vulnerabilities. Here are some key aspects of proactive hardening: Reactive Security Hardening Reactive security hardening, on the other hand, is a response to a security incident or breach. It involves taking immediate actions to contain and mitigate the impact of an attack. Here are the key aspects of reactive hardening: Proactive vs. Reactive: Key Differences Now that we’ve explored both proactive and reactive security hardening, let’s highlight their key differences: In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, both proactive and reactive security hardening strategies are essential. Proactive measures fortify your defenses and reduce the likelihood of security breaches, while reactive measures help you respond effectively when incidents inevitably occur. To create a robust cybersecurity posture, organizations should integrate both approaches, conducting regular risk assessments, implementing preventive measures, and having a well-defined incident response plan. By striking the right balance between proactive and reactive security hardening, you can better protect your digital assets and minimize the impact of potential threats.
Strengthening Your Defenses: Firewall Hardening with NSPM Solutions
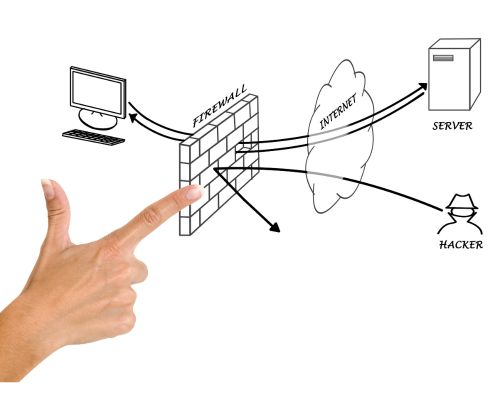
In today’s digital age, where cyber threats continue to evolve at an alarming rate, safeguarding your organization’s data and network integrity is more critical than ever. Firewalls play a pivotal role in fortifying your cyber defenses, acting as a barrier between your internal network and the outside world. However, firewalls themselves require continuous reinforcement to remain effective against emerging threats. In this blog post, we’ll explore the concept of firewall hardening and how Network Security Policy Management(NSPM) solutions can help you achieve it. Understanding Firewall Hardening Firewall hardening is the process of strengthening the security of your firewall by minimizing vulnerabilities and enhancing its resistance to potential threats. It involves a comprehensive assessment and optimization of your firewall’s configuration, rules, and policies. The objective is to ensure that your firewall is configured to allow legitimate traffic while effectively blocking or mitigating unauthorized access and potential attacks. The Need for Hardening Achieving Firewall Hardening with NSPM Solutions Now, let’s explore how Network Security Policy Management(NSPM) solutions can help you accomplish effective firewall hardening: In a world where cybersecurity threats are a constant concern, firewall hardening is essential for safeguarding your organization’s network and data. Network Security Policy Management (NSPM) solutions offer a powerful set of tools and capabilities to help you achieve effective firewall hardening. By embracing centralized control, rule optimization, change management, policy analysis, risk assessment, automation, orchestration, and threat intelligence integration through NSPM solutions, you can ensure that your firewall remains resilient in the face of evolving threats. Remember that cybersecurity is an ongoing process, and the proactive measures discussed in this blog post will help you maintain a strong defense against the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats.
Power of Firewall Policy Optimization: Framework Models for Enhanced Cybersecurity

In the world of cybersecurity, maintaining an airtight defense is paramount. Among the critical elements of a robust defense strategy is Firewall Policy Optimization, a process that fine-tunes your firewall rules and configurations for maximum efficiency and security. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the importance of Firewall Policy Optimization and introduce you to popular framework models that can revolutionize your organization’s cybersecurity posture. Understanding Firewall Policy Optimization What is Firewall Policy Optimization? Firewall Policy Optimization is the systematic review and refinement of your organization’s firewall rules and configurations to enhance security, streamline operations, and ensure compliance with industry standards and best practices. It involves identifying and eliminating redundant, conflicting, or unnecessary rules, ensuring that firewall policies align with your organization’s security objectives. Why is it Important? Firewalls are the first line of defense against cyber threats. A well-optimized firewall policy ensures that your organization’s network is protected efficiently and effectively. Here’s why it matters: Framework Models for Firewall Policy Optimization Effective Firewall Policy Optimization requires a structured approach. Below are two popular framework models that organizations often use to achieve optimal results: 1. Center for Internet Security (CIS) Framework The CIS framework provides a comprehensive set of guidelines and best practices for securing computer systems and networks. It includes a well-defined process: a. Inventory and Documentation: b. Rule Review and Cleanup: c. Rule Creation and Modification: d. Testing and Validation: e. Documentation and Reporting: 2. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Framework NIST is a globally recognized authority on cybersecurity standards and best practices. Their framework for Firewall Policy Optimization focuses on risk management and continuous improvement: a. Risk Assessment: b. Policy Review and Revision: c. Testing and Validation: d. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement: Implementing Firewall Policy Optimization The successful implementation of Firewall Policy Optimization involves the following key steps: 1. Assessment: Begin with a comprehensive assessment of your organization’s current firewall policies, configurations, and rule sets. Identify areas where optimization can improve security and efficiency. 2. Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of firewall policies, rule descriptions, justifications, and change history. This documentation serves as a critical reference for policy optimization and compliance audits. 3. Analysis and Cleanup: Analyze existing firewall rules to identify redundancies, conflicts, and outdated rules. Eliminate unnecessary rules that no longer serve a valid business purpose. 4. Rule Creation and Modification: Create new rules based on business requirements and security policies. Modify existing rules to align with industry best practices and organizational goals. 5. Testing and Validation: Conduct testing in a controlled environment to ensure that policy changes do not disrupt operations. Validate that the optimized rules function as intended and do not introduce vulnerabilities. 6. Documentation and Reporting: Maintain ongoing documentation of firewall policies and rule changes. Generate regular reports that provide insights into policy optimization, compliance, and security posture. 7. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Implement continuous monitoring to identify emerging threats, policy deviations, or changes in network traffic patterns. Regularly review and update firewall policies to adapt to evolving threats and organizational changes. Firewall Policy Optimization is not just a best practice; it’s a critical component of an effective cybersecurity strategy. By systematically reviewing and refining your firewall policies and configurations, you can enhance security, streamline operations, ensure compliance, and achieve cost savings. The framework models provided by organizations like CIS and NIST offer a structured approach to Firewall Policy Optimization, guiding you through the process step by step. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, implementing Firewall Policy Optimization can significantly bolster your cybersecurity defenses and contribute to the overall resilience of your organization in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Guarding the Gate: Security Breaches Caused by Firewall Misconfigurations

Firewalls are the first line of defence in today’s cyberworld. They keep networks safe from unauthorised access and harmful activities. But what happens when the person who is supposed to protect you becomes the weak link? A small mistake in your firewall settings can let in huge security holes, data leaks, and money loss. This blog will discuss firewall misconfigurations, their real-world implications, and how to protect your business. Read the blog ahead to learn more! The Important Role of Firewalls A firewall is like a digital gatekeeper because it checks, filters, and controls all incoming and outgoing traffic based on rules that have already been set. When set up correctly, it keeps hackers, malware, and strange traffic out. However, a single incorrect rule or open port can undo all this protection, creating an invisible backdoor into your systems. The Hidden Risks of Incorrectly Configured Firewalls Openings That Are Not Meant to Be There: If you don’t set things up right, you could accidentally expose sensitive parts of your network. One wrong rule can let people who shouldn’t have access to private data or internal systems get in. Data Leaks: A problem with a firewall can cause huge data leaks that expose personal, business, or financial information. The damage to a company’s reputation and finances from these kinds of events can be devastating. Ransomware Breach: When bad traffic gets through because of bad settings, ransomware can get in, encrypt your data, and hold it hostage, stopping your business in its tracks. Customers Don’t Trust You Anymore: Customers expect careful handling of their information. Mistakes in configuration that lead to a breach can permanently damage credibility and relationships with clients. Fines from the Law and the Government: In industries with strict compliance rules, one mistake can lead to big fines and legal action for not following data protection rules. Problems with Operations: If a firewall is set up wrong, it might block legitimate traffic, which could cause the system to go down, workflows to be interrupted, and expensive productivity losses. What Causes Firewall Settings to Be Incorrect? Human Mistakes: Even IT admins who have been doing it for a long time can mess up when they set things up by hand. Writing something wrong or forgetting a rule can make things dangerous. Poor Documentation: Without adequate documentation, monitoring configurations and resolving issues during firewall modifications can be challenging. Adding More Complexity to the Network: As companies get bigger, their networks and rules become more complex. When there isn’t a central view, it is easy to miss misconfigurations. Not Enough Training: Firewall management needs skills. Without regular training, IT staff might lack awareness of best practices or new risks. Conflicts Arise When There Are Too Many Similar Rules: It can be hard to understand when there are too many or similar rules. Sometimes they let traffic through that shouldn’t be, or they block traffic that should be. How Misconfigured Firewalls Can Allow Unauthorised Access in the Real World Equifax (2017): Hackers were able to take advantage of a flaw in the firewall, putting the personal information of more than 147 million users at risk. Target (2013): Attackers got into Target’s network by using stolen credentials from a third-party vendor. A misconfigured firewall made this possible. Airbus Defence and Space (2016): Incorrectly set rules made important research data from more than a decade available to people who shouldn’t have had access to it. How to Stop Firewall Settings from Going Wrong Do Regular Audits of Your Firewall: Set up regular audits to find and fix configuration problems as soon as possible. Automated tools can make this process easier and identify mistakes that people might miss. Make Sure Access Control Is Followed: Only people who are allowed to manage the firewall should be able to do so. Use Access Control Lists (ACLs) to cut down on mistakes made by people. Keep Thorough Records: Document every rule and change. It’s easier to review configurations and avoid conflicts when they are clearly documented. Train Your Staff: Learning never stops. Let your IT team know about new threats, tools, and best practices for firewalls analysis. Use Tools for Centralised Management: Use solutions that let you see everything across all of your firewalls. This makes it easier to set up, check, and keep an eye on things. Check Before You Deploy: Make a sandbox or test environment to safely test new rules before putting them into use on live systems. Update Your Software: Always install the most recent firmware and security patches to fix known security holes and improve control over your settings. Final Conclusion: Stay Safe and Watch Out How strong a firewall is depends on how it is set up. In a time when cyber threats change every day, businesses can’t afford to let small mistakes turn into big problems. Regular audits, excellent record-keeping, constant training, and managing everything from one place are all ways to make sure your firewalls stay true guardians of your digital perimeter and not gateways for attackers. Are you ready to improve your computer security? Talk to Opinnate right away!
Navigating the Digital Peril: Safeguarding Against Cybersecurity Threats and Essential Precautions

In our technology-driven era, the digital landscape offers unprecedented opportunities for growth and connectivity. Yet, this landscape is also rife with potential hazards in the form of cyber threats that can wreak havoc on personal and organizational data. As the stakes continue to rise, understanding these threats and adopting crucial precautions becomes paramount. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the dynamic realm of cybersecurity threats and unveil essential measures to fortify your digital defenses. Unveiling the Landscape of Cybersecurity Threats The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, with malicious actors employing innovative techniques to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access. It’s crucial to comprehend the breadth of these threats to adequately prepare against them: Essential Precautions to Bolster Cybersecurity In the face of these multifaceted threats, taking proactive measures to safeguard your digital assets and sensitive information is non-negotiable. Here are crucial precautions that individuals and organizations should implement: 1. Keep Software Updated: Regularly update operating systems, applications, and security software to patch vulnerabilities. Attackers often target outdated software with known weaknesses. 2. Strong Password Practices: Implement robust password policies that encourage the use of complex passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA). Change passwords periodically and never reuse them across accounts. 3. Security Awareness Training: Educate employees, contractors, and users about cybersecurity best practices. Training can help individuals recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other threats. 4. Regular Data Backups: Frequently back up critical data to offline or secure cloud storage. This precaution can mitigate the impact of ransomware attacks and data loss incidents. 5. Network Segmentation: Segment your network into isolated zones, limiting lateral movement for attackers. This strategy can mitigate the spread of threats across your infrastructure. 6. Firewall and Intrusion Detection Systems: Deploy firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activities. These tools can detect and prevent unauthorized access attempts. 7. Endpoint Security: Install and update antivirus software, anti-malware solutions, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools on all devices connected to your network. 8. Secure Web Browsing: Enable safe browsing features on web browsers to prevent users from visiting malicious websites. Additionally, utilize web filtering to block access to risky or inappropriate sites. 9. Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan outlining steps to take in the event of a cyber attack. Test the plan through simulated exercises to ensure its effectiveness. 10. Vendor Security Assessment: Assess the cybersecurity measures of third-party vendors and partners before sharing sensitive information or granting access to your network. 11. Encrypt Data: Implement encryption for sensitive data, both during transit and while at rest. Encryption adds an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access. 12. Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits to assess vulnerabilities, evaluate the effectiveness of existing measures, and identify areas for improvement. 13. Employee Vigilance: Encourage a culture of cybersecurity awareness among employees. Instill caution regarding email attachments, links, and requests for sensitive information. 14. Patch Management: Maintain a robust patch management strategy to ensure that all software and systems are up to date with the latest security patches. The Path to a More Secure Digital Future As cyber threats grow in complexity and frequency, adopting a proactive stance in cybersecurity is no longer optional – it’s imperative. By understanding the diverse range of threats and implementing the essential precautions outlined above, individuals and organizations can fortify their digital defenses and mitigate the risks posed by malicious actors. Remember, cybersecurity is a continuous effort. Regularly review and adapt your strategies to stay ahead of evolving threats. By embracing these precautions and fostering a culture of vigilance, you can navigate the digital landscape with confidence, knowing that you’ve taken significant steps to safeguard your digital assets and sensitive information.


